
Revenue is the money generated by a company during a period but before operating expenses and overhead costs are deducted. In some industries, revenue is called gross sales because the gross figure is calculated before any deductions. Profits give a lot of room to the business owner(s) or the company management to use the surplus money earned.
What Is Retained Earnings to Market Value?
- Such a balance can be both positive or negative, depending on the net profit or losses made by the company over the years and the amount of dividend paid.
- Retained earnings act as a reservoir of internal financing you can use to fund growth initiatives, finance capital expenditures, repay debts, or hire new staff.
- A statement of retained earnings details the changes in a company’s retained earnings balance over a specific period, usually a year.
- Hence retained earnings are the company’s past earnings that have been kept by the company instead of being distributed to shareholders as dividends.
- In this case, this debit balance of retained earnings will be presented as a negative in the balance sheet.
Once your cost of goods sold, expenses, and any liabilities are covered, you have to pay out cash dividends to shareholders. The money that’s left after you’ve paid your shareholders is held onto (or “retained”) by the business. Retained Earnings (RE) are the accumulated portion of a business’s profits that are not distributed as dividends to shareholders but instead are reserved for reinvestment back into the business. Normally, these funds are used for working capital and fixed asset purchases (capital expenditures) or allotted for paying off debt obligations. When a company generates net income, it is typically recorded as a credit to the retained earnings account, increasing the balance. In contrast, when a company suffers a net loss or pays dividends, the retained earnings account is debited, reducing the balance.
Limitations of Retained Earnings
First, you have to figure out the fair market value (FMV) of the shares you’re distributing. Companies will also usually issue a percentage of all their stock as a dividend (i.e. a 5% stock dividend means is retained earning a debit or credit you’re giving away 5% of the company’s equity). The RE balance may not always be a positive number, as it may reflect that the current period’s net loss is greater than that of the RE beginning balance.
Retained earnings explained

Expenses are grouped toward the bottom of the income statement, and net income (bottom line) is on the last line of the statement. Businesses that generate retained earnings over time are more valuable and have greater financial flexibility. It’s safe to say that understanding the retained earnings equation and how to calculate it is essential for any business. This article provides a comprehensive overview of what you need to know about retained earnings, but feel free to jump straight to your topic of focus below. While a t-shirt can remain essentially unchanged for a long period of time, a computer or smartphone requires more regular advancement to stay competitive within the market.
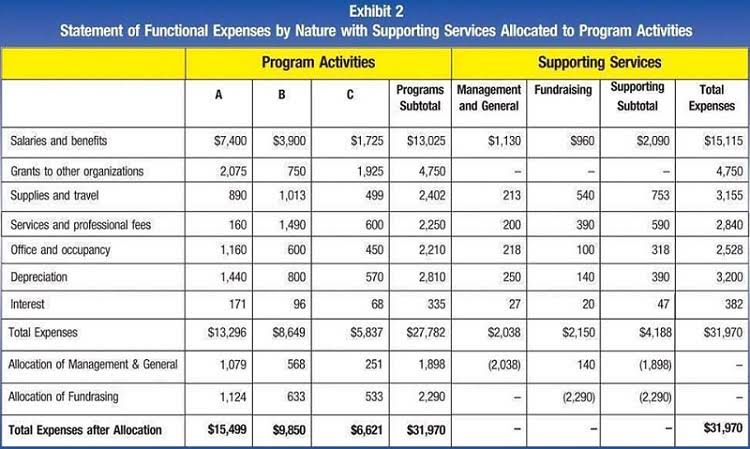
These statements report changes to your retained earnings over the course of an accounting period. When a company consistently retains part of its earnings and demonstrates a history of profitability, it’s a good indicator of financial health and growth potential. This can make a business more appealing to investors who are seeking long-term value and a return on their investment. These programs are designed to assist small businesses with creating financial statements, including retained earnings. First, revenue refers to the total amount of money generated by a company.
- Up-to-date financial reporting helps you keep an eye on your business’s financial health so you can identify cash flow issues before they become a problem.
- Samsung Inc. earned a net profit of 500,000 during the accounting period Jan-Dec 20×1.
- Stock dividends are payments made in the form of additional shares paid out to investors.
- One piece of financial data that can be gleaned from the statement of retained earnings is the retention ratio.
How to Calculate Dividends, Retained Earnings and Statement of Cash Flow
Net Income is the profit your company made during the current period after all expenses have been deducted from revenues. Now that you’ve learned how to calculate retained earnings, accuracy is key. The purpose of a balance sheet is to ensure all your bookkeeping journal entries are correct and every penny is accounted for. The income statement calculates net income, which is the balance you have after subtracting additional expenses from the gross profit.

A statement of retained earnings details the changes in a company’s retained earnings balance over a specific period, usually a year. Retained earnings refer to the money your company keeps for itself after paying out dividends to shareholders. Retained earnings, at their core, are the portion of a company’s net income that remains after all dividends and distributions to shareholders are paid out.

Generally speaking, a company with a negative retained earnings balance would signal weakness because it indicates that the company has experienced losses in one or more previous years. However, it is more difficult to interpret a company with high retained earnings. Management and shareholders may want the company to retain earnings for several different reasons. Retained earnings are also called earnings surplus and represent reserve money, which is available to company management for reinvesting back into the business. When expressed as a percentage of total earnings, it is also called the retention ratio and is equal to (1 – the dividend payout ratio). Often during a company’s startup years, it can have a negative balance in its retained earnings.
- After those obligations are paid, a company can determine whether it has positive or negative retained earnings.
- There can be cases where a company may have a negative retained earnings balance.
- Though retained earnings are not an asset, they can be used to purchase assets in order to help a company grow its business.
- On the other hand, retained earnings is a “bottom-line” reporting account that is only calculated after all other calculations have been settled.
These expenses often go hand-in-hand with the manufacture and distribution of products. For example, a company may pay facilities costs for its corporate headquarters; by selling products, the company hopes to pay its facilities costs and have money left over. Generally speaking, the par value of common stock is minimal and has no economic significance. However, if a state law requires a par (or stated) value, the accountant is required to record the par (or stated) value of the common stock in the account Common Stock. If every transaction you post keeps the formula balanced, you can generate an accurate balance sheet. Regularly assess your retained earnings in the context of your business objectives and shareholder needs, perhaps with the help of financial advisors.

Comentários